category
The OAuth 2.0 authorization code grant type, or auth code flow, enables a client application to obtain authorized access to protected resources like web APIs. The auth code flow requires a user-agent that supports redirection from the authorization server (the Microsoft identity platform) back to your application. For example, a web browser, desktop, or mobile application operated by a user to sign in to your app and access their data.
This article describes low-level protocol details required only when manually crafting and issuing raw HTTP requests to execute the flow, which we do not recommend. Instead, use a Microsoft-built and supported authentication library to get security tokens and call protected web APIs in your apps.
Applications that support the auth code flow
Use the auth code flow paired with Proof Key for Code Exchange (PKCE) and OpenID Connect (OIDC) to get access tokens and ID tokens in these types of apps:
Protocol details
The OAuth 2.0 authorization code flow is described in section 4.1 of the OAuth 2.0 specification. Apps using the OAuth 2.0 authorization code flow acquire an access_token to include in requests to resources protected by the Microsoft identity platform (typically APIs). Apps can also request new ID and access tokens for previously authenticated entities by using a refresh mechanism.
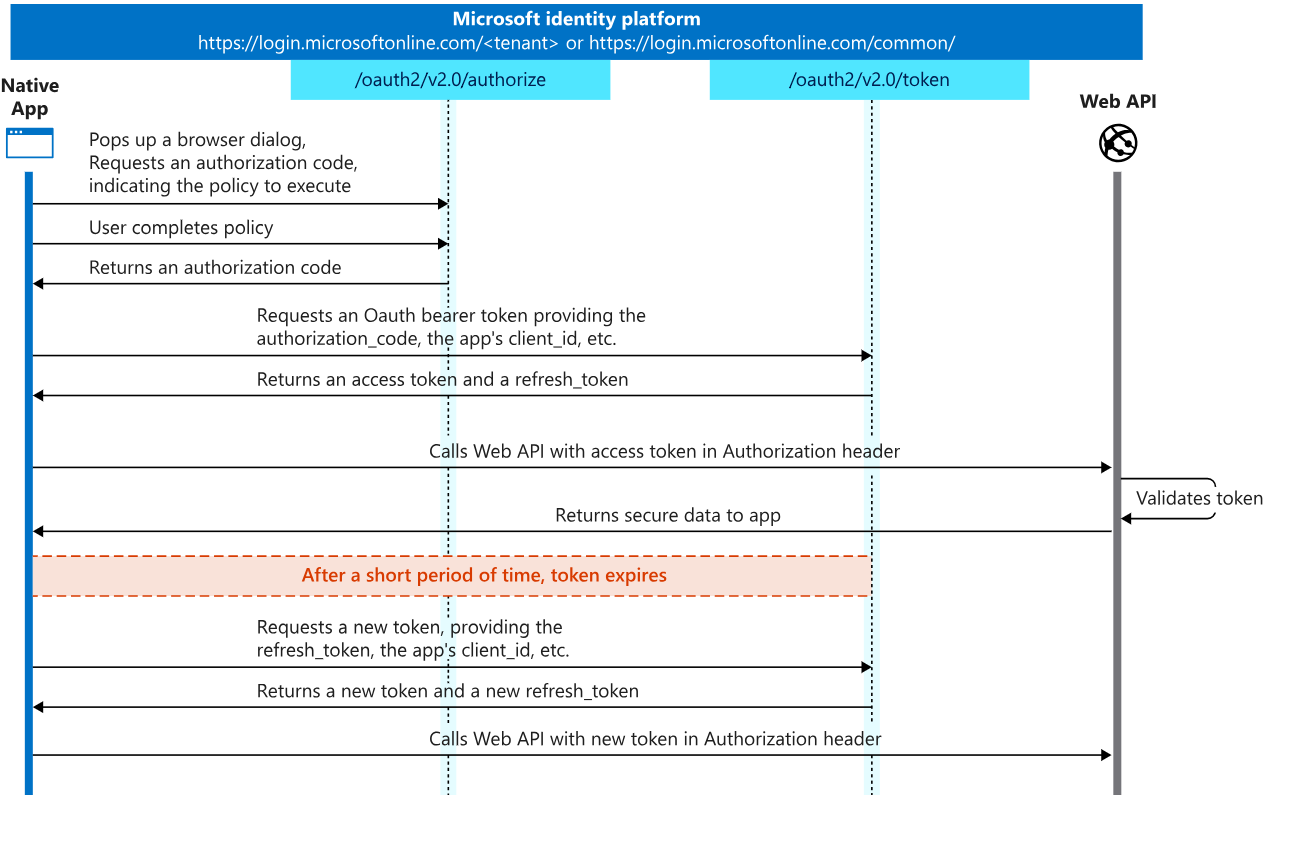
This diagram shows a high-level view of the authentication flow:
Redirect URIs for single-page apps (SPAs)
Redirect URIs for SPAs that use the auth code flow require special configuration.
- Add a redirect URI that supports auth code flow with PKCE and cross-origin resource sharing (CORS): Follow the steps in Redirect URI: MSAL.js 2.0 with auth code flow.
- Update a redirect URI: Set the redirect URI's
typetospaby using the application manifest editor in the Microsoft Entra admin center.
The spa redirect type is backward-compatible with the implicit flow. Apps currently using the implicit flow to get tokens can move to the spa redirect URI type without issues and continue using the implicit flow.
If you attempt to use the authorization code flow without setting up CORS for your redirect URI, you'll see this error in the console:
access to XMLHttpRequest at 'https://login.microsoftonline.com/common/v2.0/oauth2/token' from origin
'yourApp.com' has been blocked by CORS policy: No 'Access-Control-Allow-Origin' header is present on the requested resource.
If so, visit your app registration and update the redirect URI for your app to use the spa type.
Applications can't use a spa redirect URI with non-SPA flows, for example, native applications or client credential flows. To ensure security and best practices, the Microsoft identity platform returns an error if you attempt to use a spa redirect URI without an Origin header. Similarly, the Microsoft identity platform also prevents the use of client credentials in all flows in the presence of an Origin header, to ensure that secrets aren't used from within the browser.
Request an authorization code
The authorization code flow begins with the client directing the user to the /authorize endpoint. In this example request, the client requests the openid, offline_access, and https://graph.microsoft.com/mail.read permissions from the user.
Some permissions are admin-restricted, for example, writing data to an organization's directory by using Directory.ReadWrite.All. If your application requests access to one of these permissions from an organizational user, the user receives an error message that says they're not authorized to consent to your app's permissions. To request access to admin-restricted scopes, you should request them directly from a Global Administrator. For more information, see Admin-restricted permissions.
Unless specified otherwise, there are no default values for optional parameters. There is, however, default behavior for a request omitting optional parameters. The default behavior is to either sign in the sole current user, show the account picker if there are multiple users, or show the login page if there are no users signed in.
// Line breaks for legibility only
https://login.microsoftonline.com/{tenant}/oauth2/v2.0/authorize?
client_id=00001111-aaaa-2222-bbbb-3333cccc4444
&response_type=code
&redirect_uri=http%3A%2F%2Flocalhost%2Fmyapp%2F
&response_mode=query
&scope=https%3A%2F%2Fgraph.microsoft.com%2Fmail.read
&state=12345
&code_challenge=YTFjNjI1OWYzMzA3MTI4ZDY2Njg5M2RkNmVjNDE5YmEyZGRhOGYyM2IzNjdmZWFhMTQ1ODg3NDcxY2Nl
&code_challenge_method=S256
| Parameter | Required/optional | Description |
|---|---|---|
tenant |
required | The {tenant} value in the path of the request can be used to control who can sign into the application. Valid values are common, organizations, consumers, and tenant identifiers. For guest scenarios where you sign a user from one tenant into another tenant, you must provide the tenant identifier to sign them into the resource tenant. For more information, see Endpoints. |
client_id |
required | The Application (client) ID that the Microsoft Entra admin center – App registrations experience assigned to your app. |
response_type |
required | Must include code for the authorization code flow. Can also include id_token or token if using the hybrid flow. |
redirect_uri |
required | The redirect_uri of your app, where authentication responses can be sent and received by your app. It must exactly match one of the redirect URIs you registered in the Microsoft Entra admin center, except it must be URL-encoded. For native and mobile apps, use one of the recommended values: https://login.microsoftonline.com/common/oauth2/nativeclient for apps using embedded browsers or http://localhost for apps that use system browsers. |
scope |
required | A space-separated list of scopes that you want the user to consent to. For the /authorize leg of the request, this parameter can cover multiple resources. This value allows your app to get consent for multiple web APIs you want to call. |
response_mode |
recommended | Specifies how the identity platform should return the requested token to your app. Supported values: - query: Default when requesting an access token. Provides the code as a query string parameter on your redirect URI. The query parameter isn't supported when requesting an ID token by using the implicit flow.- fragment: Default when requesting an ID token by using the implicit flow. Also supported if requesting only a code.- form_post: Executes a POST containing the code to your redirect URI. Supported when requesting a code. |
state |
recommended | A value included in the request that is also returned in the token response. It can be a string of any content that you wish. A randomly generated unique value is typically used for preventing cross-site request forgery attacks. The value can also encode information about the user's state in the app before the authentication request occurred. For instance, it could encode the page or view they were on. |
prompt |
optional | Indicates the type of user interaction that is required. Valid values are login, none, consent, and select_account.- prompt=login forces the user to enter their credentials on that request, negating single-sign on.- prompt=none is the opposite. It ensures that the user isn't presented with any interactive prompt. If the request can't be completed silently by using single-sign on, the Microsoft identity platform returns an interaction_required error.- prompt=consent triggers the OAuth consent dialog after the user signs in, asking the user to grant permissions to the app.- prompt=select_account interrupts single sign-on providing account selection experience listing all the accounts either in session or any remembered account or an option to choose to use a different account altogether. |
login_hint |
optional | You can use this parameter to pre-fill the username and email address field of the sign-in page for the user. Apps can use this parameter during reauthentication, after already extracting the login_hint optional claim from an earlier sign-in. |
domain_hint |
optional | If included, the app skips the email-based discovery process that user goes through on the sign-in page, leading to a slightly more streamlined user experience. For example, sending them to their federated identity provider. Apps can use this parameter during reauthentication, by extracting the tid from a previous sign-in. |
code_challenge |
recommended / required | Used to secure authorization code grants by using Proof Key for Code Exchange (PKCE). Required if code_challenge_method is included. For more information, see the PKCE RFC. This parameter is now recommended for all application types, both public and confidential clients, and required by the Microsoft identity platform for single page apps using the authorization code flow. |
code_challenge_method |
recommended / required | The method used to encode the code_verifier for the code_challenge parameter. This SHOULD be S256, but the spec allows the use of plain if the client can't support SHA256.If excluded, code_challenge is assumed to be plaintext if code_challenge is included. The Microsoft identity platform supports both plain and S256. For more information, see the PKCE RFC. This parameter is required for single page apps using the authorization code flow. |
At this point, the user is asked to enter their credentials and complete the authentication. The Microsoft identity platform also ensures that the user has consented to the permissions indicated in the scope query parameter. If the user hasn't consented to any of those permissions, it asks the user to consent to the required permissions. For more information, see Permissions and consent in the Microsoft identity platform.
Once the user authenticates and grants consent, the Microsoft identity platform returns a response to your app at the indicated redirect_uri, using the method specified in the response_mode parameter.
Successful response
This example shows a successful response using response_mode=query:
GET http://localhost?
code=AwABAAAAvPM1KaPlrEqdFSBzjqfTGBCmLdgfSTLEMPGYuNHSUYBrq...
&state=12345
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
code |
The authorization_code that the app requested. The app can use the authorization code to request an access token for the target resource. Authorization codes are short lived. Typically, they expire after about 10 minutes. |
state |
If a state parameter is included in the request, the same value should appear in the response. The app should verify that the state values in the request and response are identical. |
You can also receive an ID token if you request one and have the implicit grant enabled in your application registration. This behavior is sometimes referred to as the hybrid flow. It's used by frameworks like ASP.NET.
Error response
Error responses may also be sent to the redirect_uri so the app can handle them appropriately:
GET http://localhost?
error=access_denied
&error_description=the+user+canceled+the+authentication
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
error |
An error code string that can be used to classify types of errors, and to react to errors. This part of the error is provided so that the app can react appropriately to the error, but doesn't explain in depth why an error occurred. |
error_description |
A specific error message that can help a developer identify the cause of an authentication error. This part of the error contains most of the useful information about why the error occurred. |
Error codes for authorization endpoint errors
The following table describes the various error codes that can be returned in the error parameter of the error response.
| Error Code | Description | Client Action |
|---|---|---|
invalid_request |
Protocol error, such as a missing required parameter. | Fix and resubmit the request. This error is a development error typically caught during initial testing. |
unauthorized_client |
The client application isn't permitted to request an authorization code. | This error usually occurs when the client application isn't registered in Microsoft Entra ID or isn't added to the user's Microsoft Entra tenant. The application can prompt the user with instruction for installing the application and adding it to Microsoft Entra ID. |
access_denied |
Resource owner denied consent | The client application can notify the user that it can't continue unless the user consents. |
unsupported_response_type |
The authorization server doesn't support the response type in the request. | Fix and resubmit the request. This error is a development error typically caught during initial testing. In the hybrid flow, this error signals that you must enable the ID token implicit grant setting on the client app registration. |
server_error |
The server encountered an unexpected error. | Retry the request. These errors can result from temporary conditions. The client application might explain to the user that its response is delayed to a temporary error. |
temporarily_unavailable |
The server is temporarily too busy to handle the request. | Retry the request. The client application might explain to the user that its response is delayed because of a temporary condition. |
invalid_resource |
The target resource is invalid because it doesn't exist, Microsoft Entra ID can't find it, or it's not correctly configured. | This error indicates the resource, if it exists, hasn't been configured in the tenant. The application can prompt the user with instruction for installing the application and adding it to Microsoft Entra ID. |
login_required |
Too many or no users found. | The client requested silent authentication (prompt=none), but a single user couldn't be found. This error may mean there are multiple users active in the session, or no users. This error takes into account the tenant chosen. For example, if there are two Microsoft Entra accounts active and one Microsoft account, and consumers is chosen, silent authentication works. |
interaction_required |
The request requires user interaction. | Another authentication step or consent is required. Retry the request without prompt=none. |
Request an ID token as well or hybrid flow
To learn who the user is before redeeming an authorization code, it's common for applications to also request an ID token when they request the authorization code. This approach is called the hybrid flow because it mixes OIDC with the OAuth2 authorization code flow.
The hybrid flow is commonly used in web apps to render a page for a user without blocking on code redemption, notably in ASP.NET. Both single-page apps and traditional web apps benefit from reduced latency in this model.
The hybrid flow is the same as the authorization code flow described earlier but with three additions. All of these additions are required to request an ID token: new scopes, a new response_type, and a new nonce query parameter.
// Line breaks for legibility only
https://login.microsoftonline.com/{tenant}/oauth2/v2.0/authorize?
client_id=00001111-aaaa-2222-bbbb-3333cccc4444
&response_type=code%20id_token
&redirect_uri=http%3A%2F%2Flocalhost%2Fmyapp%2F
&response_mode=fragment
&scope=openid%20offline_access%20https%3A%2F%2Fgraph.microsoft.com%2Fuser.read
&state=12345
&nonce=abcde
&code_challenge=YTFjNjI1OWYzMzA3MTI4ZDY2Njg5M2RkNmVjNDE5YmEyZGRhOGYyM2IzNjdmZWFhMTQ1ODg3NDcxY2Nl
&code_challenge_method=S256
| Updated Parameter | Required/optional | Description |
|---|---|---|
response_type |
required | The addition of id_token indicates to the server that the application would like an ID token in the response from the /authorize endpoint. |
scope |
required | For ID tokens, this parameter must be updated to include the ID token scopes: openid and optionally profile and email. |
nonce |
required | A value included in the request, generated by the app, that is included in the resulting id_token as a claim. The app can then verify this value to mitigate token replay attacks. The value is typically a randomized, unique string that can be used to identify the origin of the request. |
response_mode |
recommended | Specifies the method that should be used to send the resulting token back to your app. Default value is query for just an authorization code, but fragment if the request includes an id_token response_type as specified in the OpenID spec. We recommend apps use form_post, especially when using http://localhost as a redirect URI. |
The use of fragment as a response mode causes issues for web apps that read the code from the redirect. Browsers don't pass the fragment to the web server. In these situations, apps should use the form_post response mode to ensure that all data is sent to the server.
Successful response
This example shows a successful response using response_mode=fragment:
GET https://login.microsoftonline.com/common/oauth2/nativeclient#
code=AwABAAAAvPM1KaPlrEqdFSBzjqfTGBCmLdgfSTLEMPGYuNHSUYBrq...
&id_token=eYj...
&state=12345
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
code |
The authorization code that the app requested. The app can use the authorization code to request an access token for the target resource. Authorization codes are short lived, typically expiring after about 10 minutes. |
id_token |
An ID token for the user, issued by using the implicit grant. Contains a special c_hash claim that is the hash of the code in the same request. |
state |
If a state parameter is included in the request, the same value should appear in the response. The app should verify that the state values in the request and response are identical. |
Redeem a code for an access token
All confidential clients have a choice of using client secrets or certificate credentials. Symmetric shared secrets are generated by the Microsoft identity platform. Certificate credentials are asymmetric keys uploaded by the developer. For more information, see Microsoft identity platform application authentication certificate credentials.
For best security, we recommend using certificate credentials. Public clients, which include native applications and single page apps, must not use secrets or certificates when redeeming an authorization code. Always ensure that your redirect URIs include the type of application and are unique.
Request an access token with a client_secret
Now that you've acquired an authorization_code and have been granted permission by the user, you can redeem the code for an access_token to the resource. Redeem the code by sending a POST request to the /token endpoint:
// Line breaks for legibility only
POST /{tenant}/oauth2/v2.0/token HTTP/1.1
Host: https://login.microsoftonline.com
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
client_id=11112222-bbbb-3333-cccc-4444dddd5555
&scope=https%3A%2F%2Fgraph.microsoft.com%2Fmail.read
&code=OAAABAAAAiL9Kn2Z27UubvWFPbm0gLWQJVzCTE9UkP3pSx1aXxUjq3n8b2JRLk4OxVXr...
&redirect_uri=http%3A%2F%2Flocalhost%2Fmyapp%2F
&grant_type=authorization_code
&code_verifier=ThisIsntRandomButItNeedsToBe43CharactersLong
&client_secret=sampleCredentia1s // NOTE: Only required for web apps. This secret needs to be URL-Encoded.
| Parameter | Required/optional | Description |
|---|---|---|
tenant |
required | The {tenant} value in the path of the request can be used to control who can sign into the application. Valid values are common, organizations, consumers, and tenant identifiers. For more information, see Endpoints. |
client_id |
required | The Application (client) ID that the Microsoft Entra admin center – App registrations page assigned to your app. |
scope |
optional | A space-separated list of scopes. The scopes must all be from a single resource, along with OIDC scopes (profile, openid, email). For more information, see Permissions and consent in the Microsoft identity platform. This parameter is a Microsoft extension to the authorization code flow, intended to allow apps to declare the resource they want the token for during token redemption. |
code |
required | The authorization_code that you acquired in the first leg of the flow. |
redirect_uri |
required | The same redirect_uri value that was used to acquire the authorization_code. |
grant_type |
required | Must be authorization_code for the authorization code flow. |
code_verifier |
recommended | The same code_verifier that was used to obtain the authorization_code. Required if PKCE was used in the authorization code grant request. For more information, see the PKCE RFC. |
client_secret |
required for confidential web apps | The application secret that you created in the app registration portal for your app. Don't use the application secret in a native app or single page app because a client_secret can't be reliably stored on devices or web pages. It's required for web apps and web APIs, which can store the client_secret securely on the server side. Like all parameters here, the client secret must be URL-encoded before being sent. This step is done by the SDK. For more information on URI encoding, see the URI Generic Syntax specification. The Basic auth pattern of instead providing credentials in the Authorization header, per RFC 6749 is also supported. |
Request an access token with a certificate credential
// Line breaks for legibility only
POST /{tenant}/oauth2/v2.0/token HTTP/1.1
Host: login.microsoftonline.com
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
client_id=00001111-aaaa-2222-bbbb-3333cccc4444
&scope=https%3A%2F%2Fgraph.microsoft.com%2Fmail.read
&code=OAAABAAAAiL9Kn2Z27UubvWFPbm0gLWQJVzCTE9UkP3pSx1aXxUjq3n8b2JRLk4OxVXr...
&redirect_uri=http%3A%2F%2Flocalhost%2Fmyapp%2F
&grant_type=authorization_code
&code_verifier=ThisIsntRandomButItNeedsToBe43CharactersLong
&client_assertion_type=urn%3Aietf%3Aparams%3Aoauth%3Aclient-assertion-type%3Ajwt-bearer
&client_assertion=eyJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiIsIng1dCI6Imd4OHRHeXN5amNScUtqRlBuZDdSRnd2d1pJMCJ9.eyJ{a lot of characters here}M8U3bSUKKJDEg
| Parameter | Required/optional | Description |
|---|---|---|
tenant |
required | The {tenant} value in the path of the request can be used to control who can sign into the application. Valid values are common, organizations, consumers, and tenant identifiers. For more detail, see Endpoints. |
client_id |
required | The Application (client) ID that the Microsoft Entra admin center – App registrations page assigned to your app. |
scope |
optional | A space-separated list of scopes. The scopes must all be from a single resource, along with OIDC scopes (profile, openid, email). For more information, see permissions, consent, and scopes. This parameter is a Microsoft extension to the authorization code flow. This extension allows apps to declare the resource they want the token for during token redemption. |
code |
required | The authorization_code that you acquired in the first leg of the flow. |
redirect_uri |
required | The same redirect_uri value that was used to acquire the authorization_code. |
grant_type |
required | Must be authorization_code for the authorization code flow. |
code_verifier |
recommended | The same code_verifier that was used to obtain the authorization_code. Required if PKCE was used in the authorization code grant request. For more information, see the PKCE RFC. |
client_assertion_type |
required for confidential web apps | The value must be set to urn:ietf:params:oauth:client-assertion-type:jwt-bearer to use a certificate credential. |
client_assertion |
required for confidential web apps | An assertion, which is a JSON web token (JWT), that you need to create and sign with the certificate you registered as credentials for your application. Read about certificate credentials to learn how to register your certificate and the format of the assertion. |
The parameters are same as the request by shared secret except that the client_secret parameter is replaced by two parameters: a client_assertion_type and client_assertion.
Successful response
This example shows a successful token response:
{
"access_token": "eyJ0eXAiOiJKV1QiLCJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiIsIng1dCI6Ik5HVEZ2ZEstZnl0aEV1Q...",
"token_type": "Bearer",
"expires_in": 3599,
"scope": "https%3A%2F%2Fgraph.microsoft.com%2Fmail.read",
"refresh_token": "AwABAAAAvPM1KaPlrEqdFSBzjqfTGAMxZGUTdM0t4B4...",
"id_token": "eyJ0eXAiOiJKV1QiLCJhbGciOiJub25lIn0.eyJhdWQiOiIyZDRkMTFhMi1mODE0LTQ2YTctOD..."
}
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
access_token |
The requested access token. The app can use this token to authenticate to the secured resource, such as a web API. |
token_type |
Indicates the token type value. The only type that Microsoft Entra ID supports is Bearer. |
expires_in |
How long the access token is valid, in seconds. |
scope |
The scopes that the access_token is valid for. Optional. This parameter is non-standard and, if omitted, the token is for the scopes requested on the initial leg of the flow. |
refresh_token |
An OAuth 2.0 refresh token. The app can use this token to acquire other access tokens after the current access token expires. Refresh tokens are long-lived. They can maintain access to resources for extended periods. For more detail on refreshing an access token, refer to Refresh the access token later in this article. Note: Only provided if offline_access scope was requested. |
id_token |
A JSON Web Token. The app can decode the segments of this token to request information about the user who signed in. The app can cache the values and display them, and confidential clients can use this token for authorization. For more information about id_tokens, see the id_token reference.Note: Only provided if openid scope was requested. |
Error response
This example is an Error response:
{
"error": "invalid_scope",
"error_description": "AADSTS70011: The provided value for the input parameter 'scope' is not valid. The scope
https://foo.microsoft.com/mail.read is not valid.\r\nTrace ID: 0000aaaa-11bb-cccc-dd22-eeeeee333333\r\nCorrelation
ID: aaaa0000-bb11-2222-33cc-444444dddddd\r\nTimestamp: 2016-01-09 02:02:12Z",
"error_codes": [
70011
],
"timestamp": "2016-01-09 02:02:12Z",
"trace_id": "0000aaaa-11bb-cccc-dd22-eeeeee333333",
"correlation_id": "aaaa0000-bb11-2222-33cc-444444dddddd"
}
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
error |
An error code string that can be used to classify types of errors, and to react to errors. |
error_description |
A specific error message that can help a developer identify the cause of an authentication error. |
error_codes |
A list of STS-specific error codes that can help in diagnostics. |
timestamp |
The time at which the error occurred. |
trace_id |
A unique identifier for the request that can help in diagnostics. |
correlation_id |
A unique identifier for the request that can help in diagnostics across components. |
Error codes for token endpoint errors
| Error Code | Description | Client Action |
|---|---|---|
invalid_request |
Protocol error, such as a missing required parameter. | Fix the request or app registration and resubmit the request. |
invalid_grant |
The authorization code or PKCE code verifier is invalid or has expired. | Try a new request to the /authorize endpoint and verify that the code_verifier parameter was correct. |
unauthorized_client |
The authenticated client isn't authorized to use this authorization grant type. | This error usually occurs when the client application isn't registered in Microsoft Entra ID or isn't added to the user's Microsoft Entra tenant. The application can prompt the user with instruction for installing the application and adding it to Microsoft Entra ID. |
invalid_client |
Client authentication failed. | The client credentials aren't valid. To fix, the Application Administrator updates the credentials. |
unsupported_grant_type |
The authorization server doesn't support the authorization grant type. | Change the grant type in the request. This type of error should occur only during development and be detected during initial testing. |
invalid_resource |
The target resource is invalid because it doesn't exist, Microsoft Entra ID can't find it, or it's not correctly configured. | This code indicates the resource, if it exists, hasn't been configured in the tenant. The application can prompt the user with instruction for installing the application and adding it to Microsoft Entra ID. |
interaction_required |
Non-standard, as the OIDC specification calls for this code only on the /authorize endpoint. The request requires user interaction. For example, another authentication step is required. |
Retry the /authorize request with the same scopes. |
temporarily_unavailable |
The server is temporarily too busy to handle the request. | Retry the request after a small delay. The client application might explain to the user that its response is delayed because of a temporary condition. |
consent_required |
The request requires user consent. This error is non-standard. It's usually only returned on the /authorize endpoint per OIDC specifications. Returned when a scope parameter was used on the code redemption flow that the client app doesn't have permission to request. |
The client should send the user back to the /authorize endpoint with the correct scope to trigger consent. |
invalid_scope |
The scope requested by the app is invalid. | Update the value of the scope parameter in the authentication request to a valid value. |
Note
Single page apps may receive an invalid_request error indicating that cross-origin token redemption is permitted only for the 'Single-Page Application' client-type. This indicates that the redirect URI used to request the token has not been marked as a spa redirect URI. Review the application registration steps on how to enable this flow.
Use the access token
Now that you have successfully acquired an access_token, you can use the token in requests to web APIs by including it in the Authorization header:
GET /v1.0/me/messages
Host: https://graph.microsoft.com
Authorization: Bearer eyJ0eXAiOiJKV1QiLCJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiIsIng1dCI6Ik5HVEZ2ZEstZnl0aEV1Q...
Refresh the access token
Access tokens are short lived. Refresh them after they expire to continue accessing resources. You can do so by submitting another POST request to the /token endpoint. Provide the refresh_token instead of the code. Refresh tokens are valid for all permissions that your client has already received consent for. For example, a refresh token issued on a request for scope=mail.read can be used to request a new access token for scope=api://contoso.com/api/UseResource.
Refresh tokens for web apps and native apps don't have specified lifetimes. Typically, the lifetimes of refresh tokens are relatively long. However, in some cases, refresh tokens expire, are revoked, or lack sufficient privileges for the action. Your application needs to expect and handle errors returned by the token issuance endpoint. Single page apps get a token with a 24-hour lifetime, requiring a new authentication every day. This action can be done silently in an iframe when third-party cookies are enabled. It must be done in a top-level frame, either full page navigation or a pop-up window, in browsers without third-party cookies, such as Safari.
Refresh tokens aren't revoked when used to acquire new access tokens. You're expected to discard the old refresh token. The OAuth 2.0 spec says: "The authorization server MAY issue a new refresh token, in which case the client MUST discard the old refresh token and replace it with the new refresh token. The authorization server MAY revoke the old refresh token after issuing a new refresh token to the client."
Important
For refresh tokens sent to a redirect URI registered as spa, the refresh token expires after 24 hours. Additional refresh tokens acquired using the initial refresh token carries over that expiration time, so apps must be prepared to re-run the authorization code flow using an interactive authentication to get a new refresh token every 24 hours. Users do not have to enter their credentials, and usually don't even see any user experience, just a reload of your application. The browser must visit the login page in a top level frame in order to see the login session. This is due to privacy features in browsers that block third party cookies.
// Line breaks for legibility only
POST /{tenant}/oauth2/v2.0/token HTTP/1.1
Host: https://login.microsoftonline.com
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
client_id=00001111-aaaa-2222-bbbb-3333cccc4444
&scope=https%3A%2F%2Fgraph.microsoft.com%2Fmail.read
&refresh_token=OAAABAAAAiL9Kn2Z27UubvWFPbm0gLWQJVzCTE9UkP3pSx1aXxUjq...
&grant_type=refresh_token
&client_secret=sampleCredentia1s // NOTE: Only required for web apps. This secret needs to be URL-Encoded
| Parameter | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
tenant |
required | The {tenant} value in the path of the request can be used to control who can sign into the application. Valid values are common, organizations, consumers, and tenant identifiers. For more information, see Endpoints. |
client_id |
required | The Application (client) ID that the Microsoft Entra admin center – App registrations experience assigned to your app. |
grant_type |
required | Must be refresh_token for this leg of the authorization code flow. |
scope |
optional | A space-separated list of scopes. The scopes requested in this leg must be equivalent to or a subset of the scopes requested in the original authorization_code request leg. If the scopes specified in this request span multiple resource server, then the Microsoft identity platform returns a token for the resource specified in the first scope. For more information, see Permissions and consent in the Microsoft identity platform. |
refresh_token |
required | The refresh_token that you acquired in the second leg of the flow. |
client_secret |
required for web apps | The application secret that you created in the app registration portal for your app. It shouldn't be used in a native app, because a client_secret can't be reliably stored on devices. It's required for web apps and web APIs, which can store the client_secret securely on the server side. This secret needs to be URL-Encoded. For more information, see the URI Generic Syntax specification. |
Successful response
This example shows a successful token response:
{
"access_token": "eyJ0eXAiOiJKV1QiLCJhbGciOiJSUzI1NiIsIng1dCI6Ik5HVEZ2ZEstZnl0aEV1Q...",
"token_type": "Bearer",
"expires_in": 3599,
"scope": "https%3A%2F%2Fgraph.microsoft.com%2Fmail.read",
"refresh_token": "AwABAAAAvPM1KaPlrEqdFSBzjqfTGAMxZGUTdM0t4B4...",
"id_token": "eyJ0eXAiOiJKV1QiLCJhbGciOiJub25lIn0.eyJhdWQiOiIyZDRkMTFhMi1mODE0LTQ2YTctOD..."
}
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
access_token |
The requested access token. The app can use this token to authenticate to the secured resource, such as a web API. |
token_type |
Indicates the token type value. The only type that Microsoft Entra ID supports is Bearer. |
expires_in |
How long the access token is valid, in seconds. |
scope |
The scopes that the access_token is valid for. |
refresh_token |
A new OAuth 2.0 refresh token. Replace the old refresh token with this newly acquired refresh token to ensure your refresh tokens remain valid for as long as possible. Note: Only provided if offline_access scope was requested. |
id_token |
An unsigned JSON Web Token. The app can decode the segments of this token to request information about the user who signed in. The app can cache the values and display them, but it shouldn't rely on them for any authorization or security boundaries. For more information about id_token, see the Microsoft identity platform ID tokens.Note: Only provided if openid scope was requested. |
Warning
Don't attempt to validate or read tokens for any API you don't own, including the tokens in this example, in your code. Tokens for Microsoft services can use a special format that will not validate as a JWT, and may also be encrypted for consumer (Microsoft account) users. While reading tokens is a useful debugging and learning tool, do not take dependencies on this in your code or assume specifics about tokens that aren't for an API you control.
Error response
{
"error": "invalid_scope",
"error_description": "AADSTS70011: The provided value for the input parameter 'scope' is not valid. The scope
https://foo.microsoft.com/mail.read is not valid.\r\nTrace ID: 0000aaaa-11bb-cccc-dd22-eeeeee333333\r\nCorrelation
ID: aaaa0000-bb11-2222-33cc-444444dddddd\r\nTimestamp: 2016-01-09 02:02:12Z",
"error_codes": [
70011
],
"timestamp": "2016-01-09 02:02:12Z",
"trace_id": "0000aaaa-11bb-cccc-dd22-eeeeee333333",
"correlation_id": "aaaa0000-bb11-2222-33cc-444444dddddd"
}
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
error |
An error code string that can be used to classify types of errors, and to react to errors. |
error_description |
A specific error message that can help a developer identify the root cause of an authentication error. |
error_codes |
A list of STS-specific error codes that can help in diagnostics. |
timestamp |
The time at which the error occurred. |
trace_id |
A unique identifier for the request that can help in diagnostics. |
correlation_id |
A unique identifier for the request that can help in diagnostics across components. |
For a description of the error codes and the recommended client action, see Error codes for token endpoint errors.
Next steps
- Go over the MSAL JS samples to get started coding.
- Learn about token exchange scenarios.
- 登录 发表评论
- 38 次浏览
最新内容
- 1 month ago
- 1 month ago
- 1 month ago
- 1 month ago
- 1 month ago
- 1 month ago
- 1 month ago
- 1 month ago
- 1 month ago
- 1 month ago