category
随着组织扩展其Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service(Amazon EKS)部署,平台管理员在高效管理多租户集群方面面临着越来越多的挑战。调查pod故障、解决资源限制和解决配置错误等任务可能会消耗大量时间和精力。团队应该专注于推动创新,而不是花费宝贵的工程时间手动解析日志、跟踪指标和实施修复。现在,有了生成式人工智能的力量,你可以改变你的Kubernetes操作。通过实施智能集群监控、模式分析和自动修复,您可以大大减少常见集群问题的平均识别时间(MTTI)和平均解决时间(MTTR)。
在AWS re:Invent 2024上,我们宣布了Amazon Bedrock的多代理协作功能(预览版)。通过多代理协作,您可以构建、部署和管理多个人工智能代理,共同完成需要专业技能的复杂多步任务。由于对EKS集群进行故障排除涉及从多个可观察性信号中获取见解,并使用连续集成和部署(CI/CD)管道应用修复,因此多代理工作流可以帮助运营团队简化EKS集群的管理。工作流管理器代理可以与各个代理集成,这些代理与各个可观察性信号和CI/CD工作流交互,以根据用户提示编排和执行任务。
在这篇文章中,我们将演示如何编排多个Amazon Bedrock代理来创建一个复杂的Amazon EKS故障排除系统。通过实现专业代理之间的协作——从K8sGPT中获取见解并通过ArgoCD框架执行操作——您可以构建一个全面的自动化系统,在最少的人为干预下识别、分析和解决集群问题。
解决方案概述
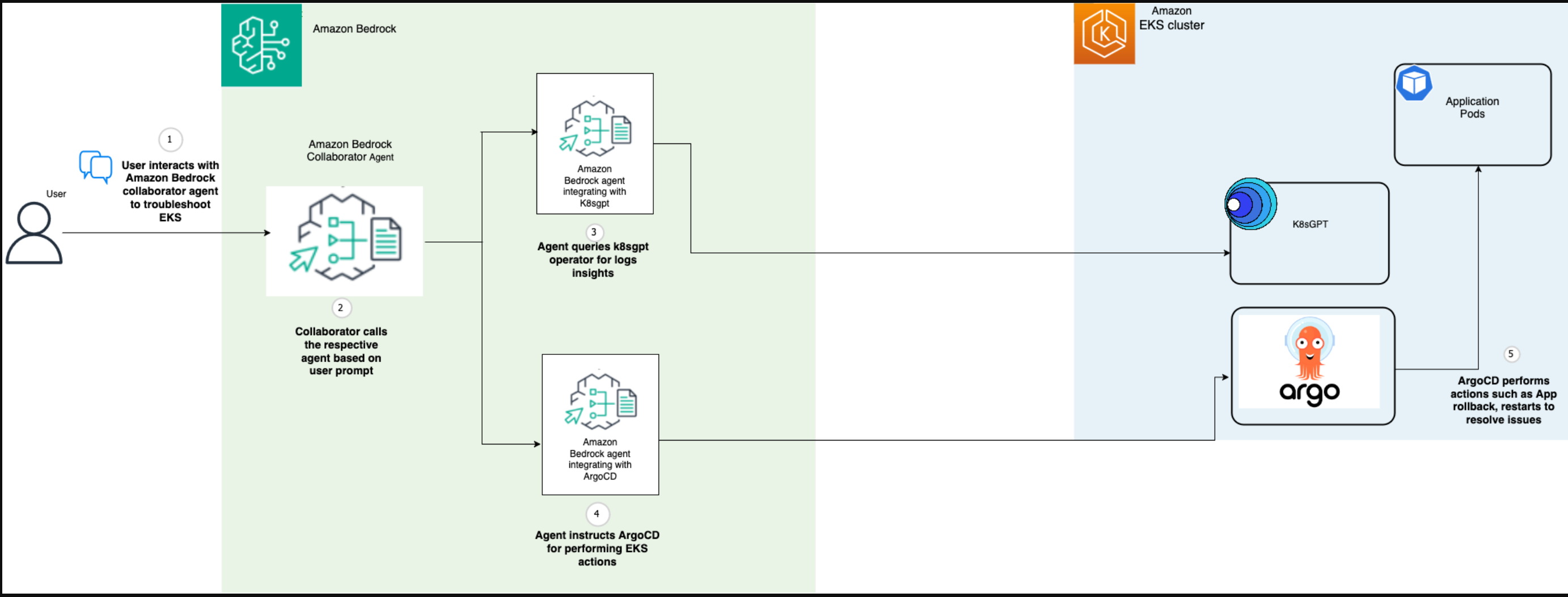
该架构由以下核心组件组成:
- Amazon Bedrock合作代理-协调工作流程并维护上下文,同时将用户提示路由到专门的代理,管理多步操作和代理交互
- 适用于K8sGPT的Amazon Bedrock代理–通过K8sGPT的Analyze API针对安全问题、错误配置和性能问题评估集群和吊舱事件,以自然语言提供补救建议
- ArgoCD的Amazon Bedrock代理–通过ArgoCD管理基于GitOps的修复,处理回滚、资源优化和配置更新
下图说明了解决方案架构。
Prerequisites
You need to have the following prerequisites in place:
- The AWS Command Line Interface (AWS CLI) version 2. For installation instructions, refer to Installing or updating to the latest version of the AWS CLI.
- An EKS cluster.
- helm.
- Kubectl.
- Amazon Bedrock model access (In this post, we used Anthropic Claude 3.5 Sonnet v1) in the AWS Region of deployment.
- Download the accompanying AWS CloudFormation template. The template is dependent on downloading resources from an Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) bucket provisioned in the US East (N. Virginia)
us-east-1AWS Region. Hence, it’s restricted to running in theus-east-1Region only.
Set up the Amazon EKS cluster with K8sGPT and ArgoCD
We start with installing and configuring the K8sGPT operator and ArgoCD controller on the EKS cluster.
The K8sGPT operator will help with enabling AI-powered analysis and troubleshooting of cluster issues. For example, it can automatically detect and suggest fixes for misconfigured deployments, such as identifying and resolving resource constraint problems in pods.
ArgoCD is a declarative GitOps continuous delivery tool for Kubernetes that automates the deployment of applications by keeping the desired application state in sync with what’s defined in a Git repository.
The Amazon Bedrock agent serves as the intelligent decision-maker in our architecture, analyzing cluster issues detected by K8sGPT. After the root cause is identified, the agent orchestrates corrective actions through ArgoCD’s GitOps engine. This powerful integration means that when problems are detected (whether it’s a misconfigured deployment, resource constraints, or scaling issue), the agent can automatically integrate with ArgoCD to provide the necessary fixes. ArgoCD then picks up these changes and synchronizes them with your EKS cluster, creating a truly self-healing infrastructure.
-
Create the necessary namespaces in Amazon EKS:
-
Add the k8sgpt Helm repository and install the operator:
-
You can verify the installation by entering the following command:
After the operator is deployed, you can configure a K8sGPT resource. This Custom Resource Definition(CRD) will have the large language model (LLM) configuration that will aid in AI-powered analysis and troubleshooting of cluster issues. K8sGPT supports various backends to help in AI-powered analysis. For this post, we use Amazon Bedrock as the backend and Anthropic’s Claude V3 as the LLM.
-
You need to create the pod identity for providing the EKS cluster access to other AWS services with Amazon Bedrock:
-
Configure the K8sGPT CRD:
-
Validate the settings to confirm the k8sgpt-bedrock pod is running successfully:
-
Now you can configure the ArgoCD controller:
-
Verify the ArgoCD installation:
-
Patch the argocd service to have an external load balancer:
-
You can now access the ArgoCD UI with the following load balancer endpoint and the credentials for the admin user:
-
Retrieve the credentials for the ArgoCD UI:
-
Push the credentials to AWS Secrets Manager:
-
Configure a sample application in ArgoCD:
-
Apply the configuration and verify it from the ArgoCD UI by logging in as the admin user:

-
It takes some time for K8sGPT to analyze the newly created pods. To make that immediate, restart the pods created in the k8sgpt-operator-system namespace. The pods can be restarted by entering the following command:
Set up the Amazon Bedrock agents for K8sGPT and ArgoCD
We use a CloudFormation stack to deploy the individual agents into the US East (N. Virginia) Region. When you deploy the CloudFormation template, you deploy several resources (costs will be incurred for the AWS resources used).
Use the following parameters for the CloudFormation template:
- EnvironmentName: The name for the deployment (EKSBlogSetup)
-
ArgoCD_LoadBalancer_URL: Extracting the ArgoCD LoadBalancer URL:
- AWSSecretName: The Secrets Manager secret name that was created to store ArgoCD credentials
The stack creates the following AWS Lambda functions:
-
<Stack name>-LambdaK8sGPTAgent-<auto-generated> <Stack name>-RestartRollBackApplicationArgoCD-<auto-generated> <Stack name>-ArgocdIncreaseMemory-<auto-generated>
The stack creates the following Amazon Bedrock agents:
ArgoCDAgent, with the following action groups:
argocd-rollbackargocd-restartargocd-memory-management
K8sGPTAgent, with the following action group:
k8s-cluster-operations
CollaboratorAgent
The stack outputs the following, with the following agents associated to it:
ArgoCDAgentK8sGPTAgent
- LambdaK8sGPTAgentRole, AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) role Amazon Resource Name (ARN) associated to the Lambda function handing interactions with the K8sGPT agent on the EKS cluster. This role ARN will be needed at a later stage of the configuration process.
K8sGPTAgentAliasId, ID of the K8sGPT Amazon Bedrock agent aliasArgoCDAgentAliasId, ID of the ArgoCD Amazon Bedrock Agent aliasCollaboratorAgentAliasId, ID of the collaborator Amazon Bedrock agent alias
Assign appropriate permissions to enable K8sGPT Amazon Bedrock agent to access the EKS cluster
To enable the K8sGPT Amazon Bedrock agent to access the EKS cluster, you need to configure the appropriate IAM permissions using Amazon EKS access management APIs. This is a two-step process: first, you create an access entry for the Lambda function’s execution role (which you can find in the CloudFormation template output section), and then you associate the AmazonEKSViewPolicy to grant read-only access to the cluster. This configuration makes sure that the K8sGPT agent has the necessary permissions to monitor and analyze the EKS cluster resources while maintaining the principle of least privilege.
-
Create an access entry for the Lambda function’s execution role
-
Associate the EKS view policy with the access entry
- Verify the Amazon Bedrock agents. The CloudFormation template adds all three required agents. To view the agents, on the Amazon Bedrock console, under Builder tools in the navigation pane, select Agents, as shown in the following screenshot.

Perform Amazon EKS troubleshooting using the Amazon Bedrock agentic workflow
Now, test the solution. We explore the following two scenarios:
- The agent coordinates with the K8sGPT agent to provide insights into the root cause of a pod failure
- The collaborator agent coordinates with the ArgoCD agent to provide a response
Agent coordinates with K8sGPT agent to provide insights into the root cause of a pod failure
In this section, we examine a down alert for a sample application called memory-demo. We’re interested in the root cause of the issue. We use the following prompt: “We got a down alert for the memory-demo app. Help us with the root cause of the issue.”
The agent not only stated the root cause, but went one step further to potentially fix the error, which in this case is increasing memory resources to the application.

Collaborator agent coordinates with ArgoCD agent to provide a response
For this scenario, we continue from the previous prompt. We feel the application wasn’t provided enough memory, and it should be increased to permanently fix the issue. We can also tell the application is in an unhealthy state in the ArgoCD UI, as shown in the following screenshot.

Let’s now proceed to increase the memory, as shown in the following screenshot.

The agent interacted with the argocd_operations Amazon Bedrock agent and was able to successfully increase the memory. The same can be inferred in the ArgoCD UI.

清理
如果您决定停止使用该解决方案,请完成以下步骤:
- 要删除使用AWS CloudFormation部署的关联资源,请执行以下操作:
- 在AWS CloudFormation控制台上,在导航窗格中选择Stacks。
- 找到您在部署过程中创建的堆栈(您为其分配了一个名称)。
- 选择堆栈并选择删除。
- 如果您专门为此实现创建了EKS集群,请删除它。
结论
通过编排多个Amazon Bedrock代理,我们演示了如何构建一个基于AI的Amazon EKS故障排除系统,简化Kubernetes操作。K8sGPT分析和ArgoCD部署自动化的集成展示了将专业AI代理与现有DevOps工具相结合的强大可能性。尽管该解决方案代表了Kubernetes自动化操作的进步,但重要的是要记住,人工监督仍然很有价值,特别是对于复杂的场景和战略决策。
随着Amazon Bedrock及其代理能力的不断发展,我们可以期待更复杂的编排可能性。您可以扩展此解决方案,以纳入其他工具、指标和自动化工作流程,以满足您组织的特定需求。
要了解有关Amazon Bedrock的更多信息,请参阅以下资源:
- 登录 发表评论
- 13 次浏览
最新内容
- 3 weeks 4 days ago
- 3 weeks 4 days ago
- 3 weeks 4 days ago
- 3 weeks 4 days ago
- 3 weeks 4 days ago
- 3 weeks 4 days ago
- 3 weeks 4 days ago
- 3 weeks 4 days ago
- 3 weeks 4 days ago
- 3 weeks 4 days ago