category
抵押贷款处理是一个复杂的、大量文档的工作流程,需要准确性、效率和合规性。传统的抵押贷款操作依赖于手动审查、基于规则的自动化和不同的系统,这往往会导致延误、错误和糟糕的客户体验。最近的行业调查显示,只有大约一半的借款人对抵押贷款过程表示满意,传统银行在借款人满意度方面落后于非银行贷款机构。满意度水平的这种差距主要归因于传统抵押贷款处理的手动、易出错的性质,其中延迟、不一致和零散的工作流程给借款人带来了沮丧,并影响了整体体验。
在这篇文章中,我们介绍了代理自动抵押贷款审批,这是一种下一代示例解决方案,它使用由亚马逊基岩代理和亚马逊基岩数据自动化支持的自主人工智能代理。这些代理协调整个抵押贷款审批流程——智能验证文件、评估风险,并在最少的人为干预下做出数据驱动的决策。通过自动化复杂的工作流程,企业可以加速审批、加快审批、最大限度地减少错误,并在提高可扩展性和合规性的同时提供一致性。
以下视频展示了这种代理自动化的实际应用,实现了更智能、更快、更可靠的大规模抵押贷款处理。
为什么选择代理IDP?
代理智能文档处理(IDP)通过提高效率和自主性,彻底改变了文档工作流程。它精确地自动化了任务,使系统能够提取、分类和处理信息,同时实时识别和纠正错误。
代理IDP超越了简单的提取,通过掌握上下文和意图,为文档添加了更深入的见解,从而推动了更明智的决策。它由Amazon Bedrock Data Automation提供支持,能够适应不断变化的文档格式和数据源,从而进一步减少人工操作。
Agent IDP专为速度和规模而构建,可快速处理大量文档,减少延迟并优化关键业务运营。它与人工智能代理和企业系统无缝集成,自动化了复杂的工作流程,降低了运营成本,使团队能够专注于高价值的战略举措。
抵押贷款处理中的IDP
抵押贷款处理涉及多个步骤,包括贷款发放、文件验证、承销和结算;每一步都需要大量的手动操作。这些步骤往往脱节,导致处理时间缓慢(几周而不是几分钟),运营成本高(手动文档审查),人为错误和欺诈的风险增加。如下图所示,组织在手动管理文档密集型工作流时面临着许多技术挑战。
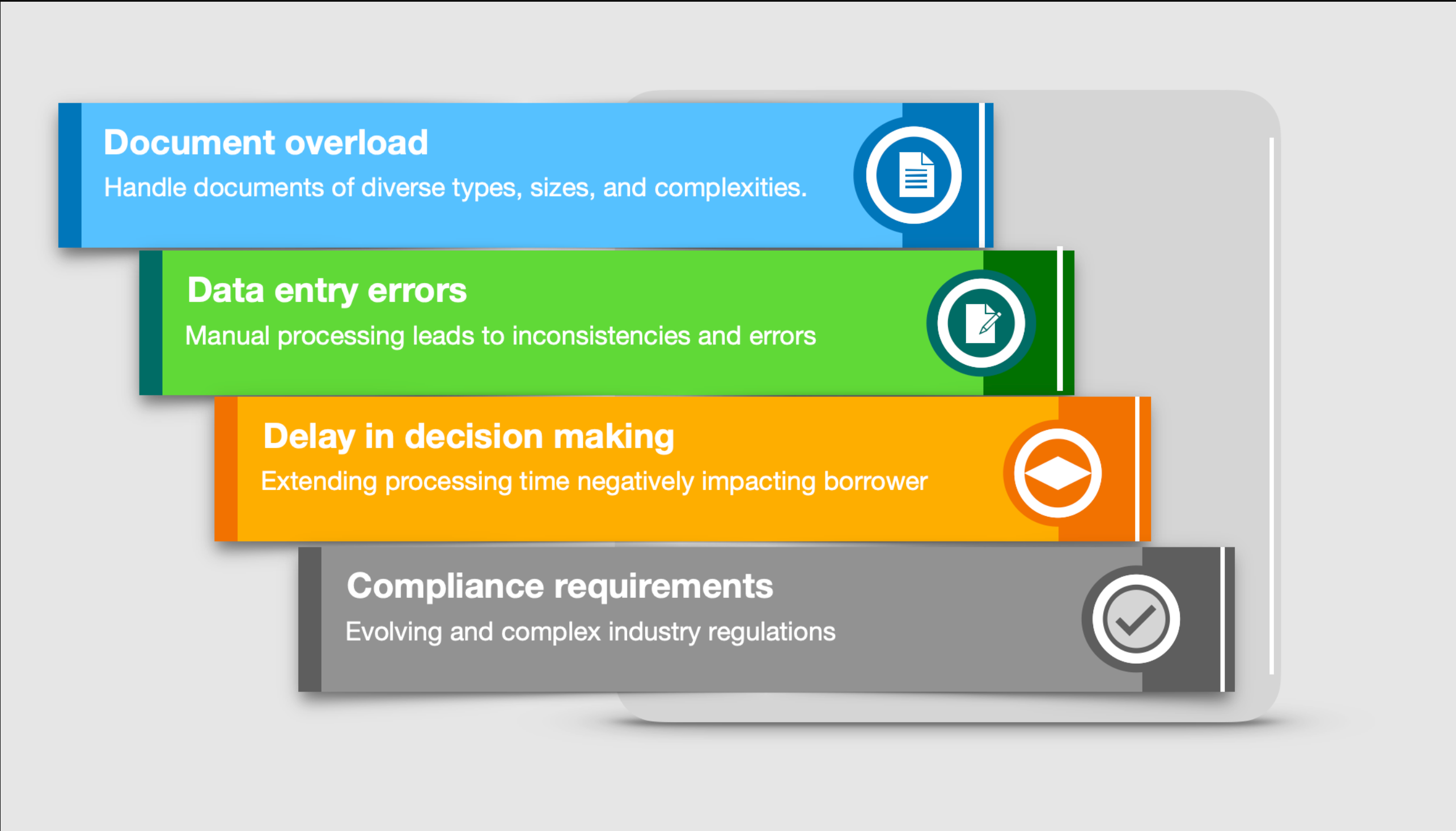
这些挑战包括:
- 文件过载——抵押贷款申请需要核实大量文件,包括税务记录、损益表、财产评估和法律协议。例如,单个抵押贷款申请可能需要手动审查和交叉验证数百页的纳税申报表、工资单、银行对账单和法律文件,这会消耗大量时间和资源。
- 数据输入错误——手动处理会在数据输入过程中引入不一致、不准确和信息缺失。W-2表格中申请人收入的错误转录或对财产评估数据的误解可能会导致贷款资格计算错误,需要昂贵的更正和返工。
- 决策延迟——人工审查流程造成的积压延长了处理时间,并对借款人的满意度产生了负面影响。贷款人手动审查收入验证和信用文件可能需要几周的时间来处理积压的工作,从而导致延误,导致失去机会或沮丧的申请人转向竞争对手。
- 监管合规的复杂性——不断演变的抵押贷款行业法规给承销和验证程序带来了复杂性。贷款法规的变化,如新的强制性披露或更新的收入验证指南,可能需要对流程进行大量的手动更新,从而导致处理时间增加、运营成本上升以及手动数据输入的错误率上升。
这些挑战凸显了自动化的必要性,以提高贷款人和抵押贷款借款人的效率、速度和准确性。
解决方案:抵押贷款处理中的代理工作流程
以下解决方案是独立的,申请人只需与抵押申请人监督代理交互,上传文件并检查或检索申请状态。下图说明了工作流程。
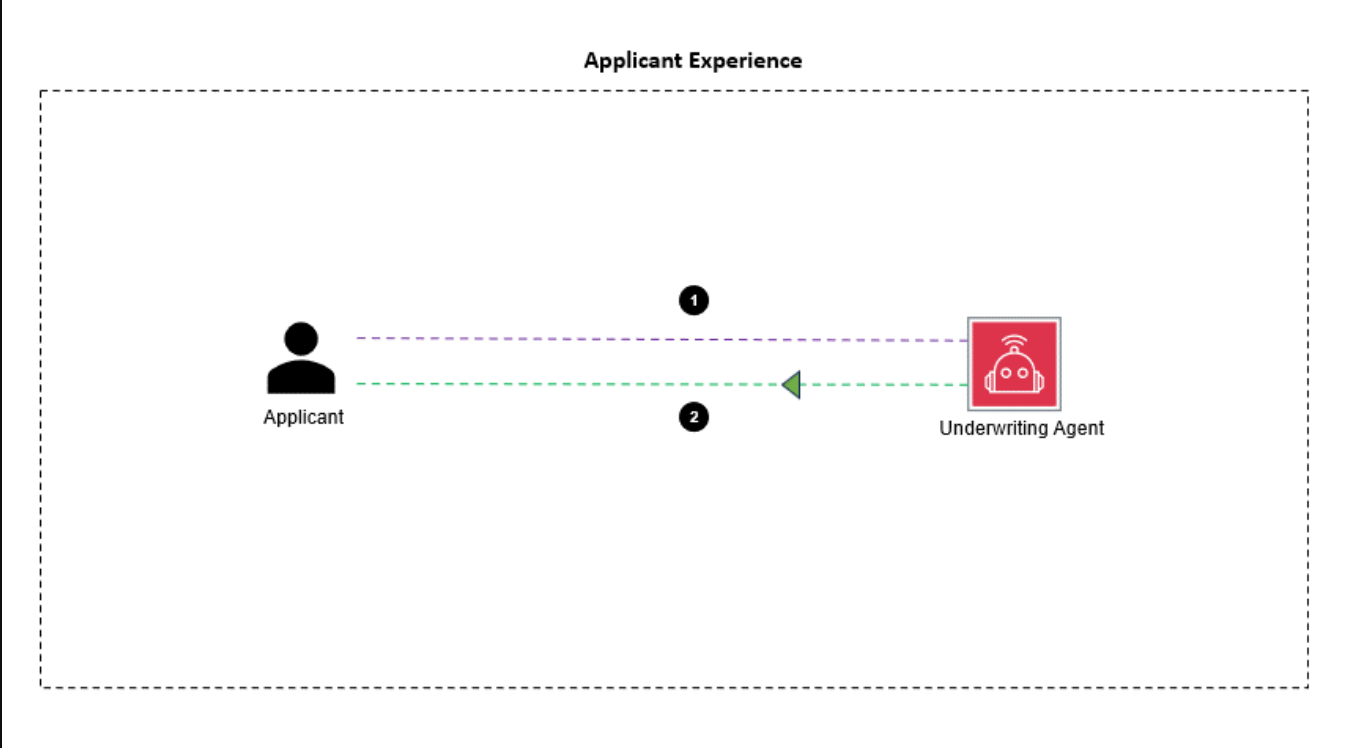
The workflow consists of the following steps:
- Applicant uploads documents to apply for a mortgage.
- The supervisor agent confirms receipt of documents. Applicant can view and retrieve application status.
- The underwriter updates the status of the application and sends approval documents to applicant.
At the core of the agentic mortgage processing workflow is a supervisor agent that orchestrates the entire workflow, manages sub-agents, and makes final decisions. Amazon Bedrock Agents is a capability within Amazon Bedrock that lets developers create AI-powered assistants capable of understanding user requests and executing complex tasks. These agents can break down requests into logical steps, interact with external tools and data sources, and use AI models to reason and take actions. They maintain conversation context while securely connecting to various APIs and AWS services, making them ideal for tasks like customer service automation, data analysis, and business process automation.
The supervisor agent intelligently delegates tasks to specialized sub-agents while maintaining the right balance between automated processing and human supervision. By aggregating insights and data from various sub-agents, the supervisor agent applies established business rules and risk criteria to either automatically approve qualifying loans or flag complex cases for human review, improving both efficiency and accuracy in the mortgage underwriting process.
In the following sections, we explore the sub-agents in more detail.
Data extraction agent
The data extraction agent uses Amazon Bedrock Data Automation to extract critical insights from mortgage application packages, including pay stubs, W-2 forms, bank statements, and identity documents. Amazon Bedrock Data Automation is a generative AI-powered capability of Amazon Bedrock that streamlines the development of generative AI applications and automates workflows involving documents, images, audio, and videos. The data extraction agent helps make sure that the validation, compliance, and decision-making agent receives accurate and structured data, enabling efficient validation, regulatory compliance, and informed decision-making. The following diagram illustrates the workflow.
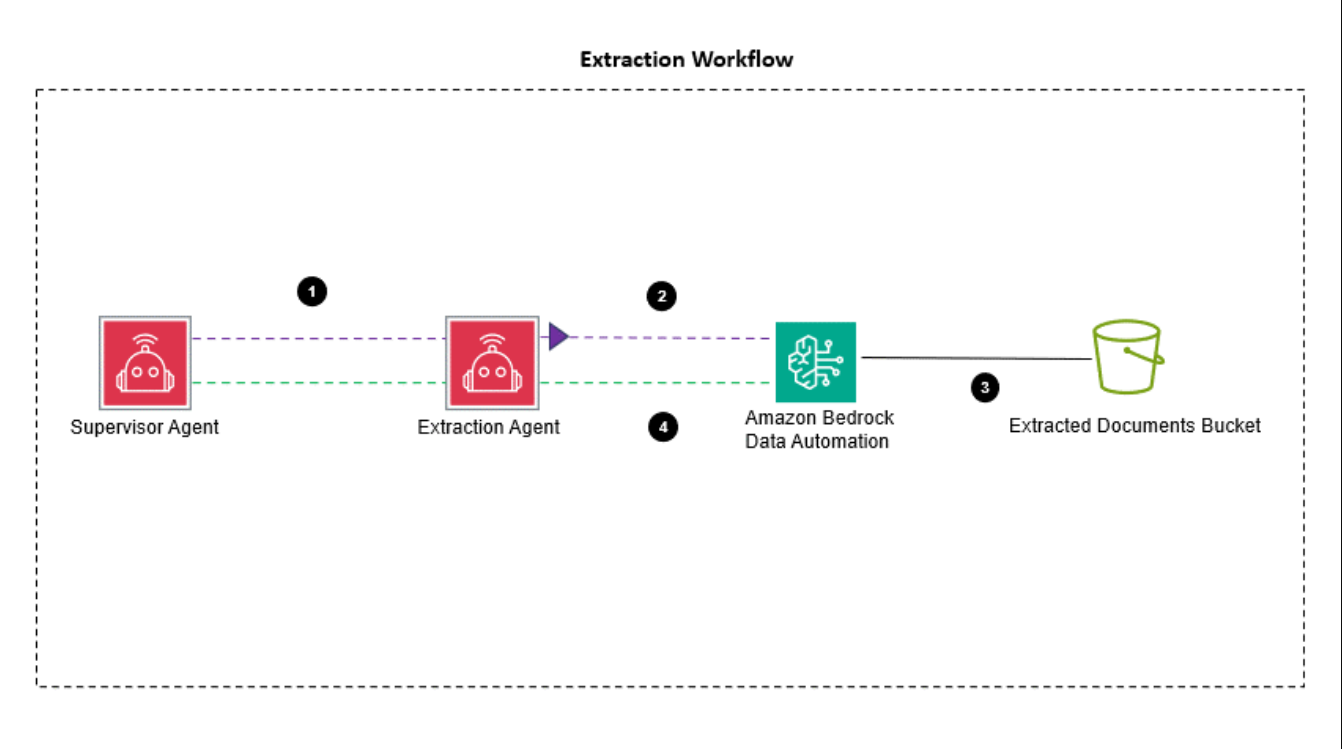
The extraction workflow is designed to automate the process of extracting data from application packages efficiently. The workflow includes the following steps:
- The supervisor agent assigns the extraction task to the data extraction agent.
- The data extraction agent invokes Amazon Bedrock Data Automation to parse and extract applicant details from the application packages.
- The extracted application information is stored in the extracted documents Amazon Simple Storage Service (Amazon S3) bucket.
- The Amazon Bedrock Data Automation invocation response is sent back to the extraction agent.
Validation agent
The validation agent cross-checks extracted data with external resources such as IRS tax records and credit reports, flagging discrepancies for review. It flags inconsistencies such as doctored PDFs, low credit score, and also calculates debt-to-income (DTI) ratio, loan-to-value (LTV) limit, and an employment stability check. The following diagram illustrates the workflow.
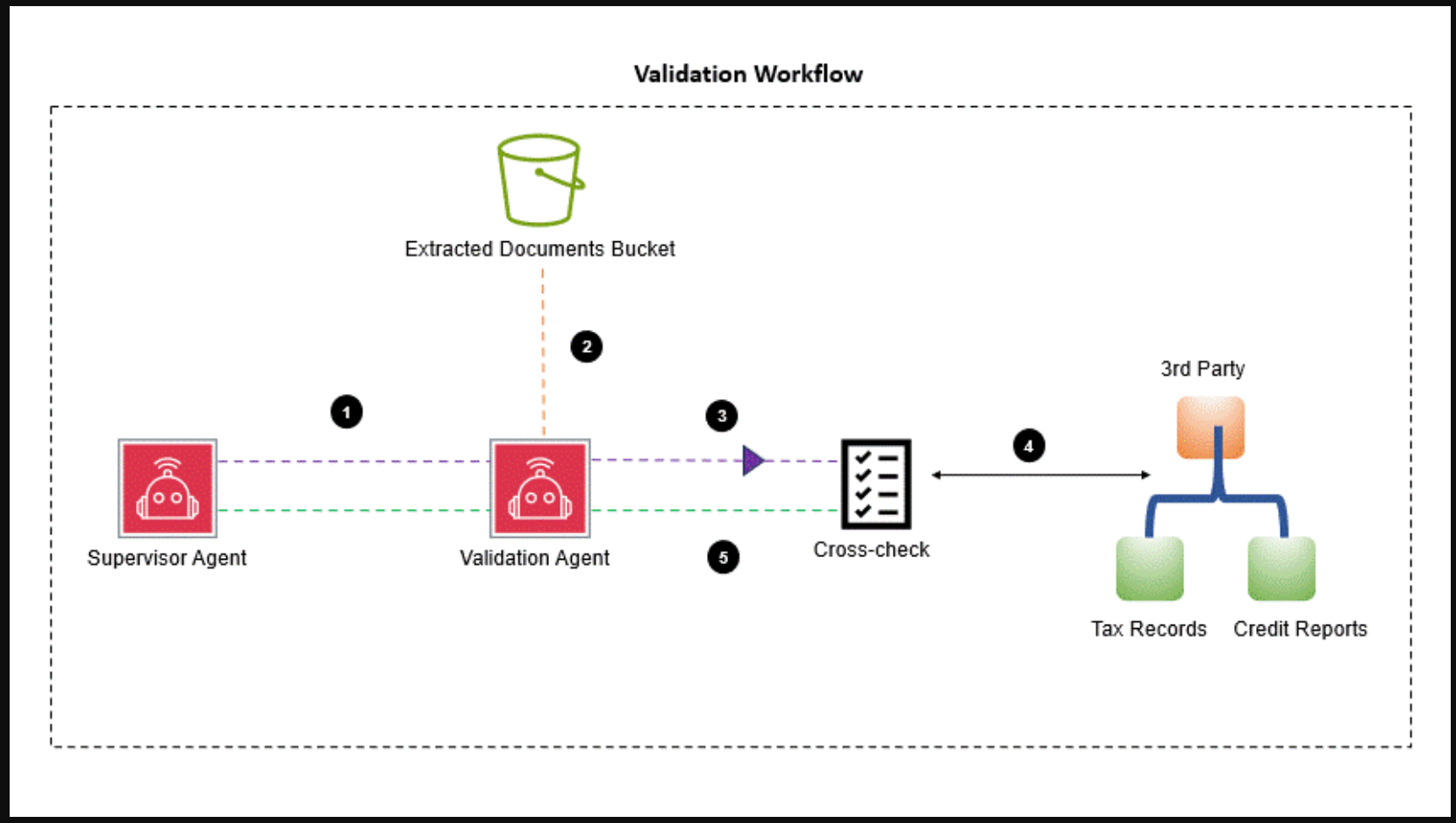
The process consists of the following steps:
- The supervisor agent assigns the validation task to the validation agent.
- The validation agent retrieves the applicant details stored in the extracted documents S3 bucket.
- The applicant details are cross-checked against third-party resources, such as tax records and credit reports, to validate the applicant’s information.
- The third-party validated details are used by the validation agent to generate a status.
- The validation agent sends the validation status to the supervisor agent.
Compliance agent
The compliance agent verifies that the extracted and validated data adheres to regulatory requirements, reducing the risk of compliance violations. It validates against lending rules. For example, loans are approved only if the borrower’s DTI ratio is below 43%, making sure they can manage monthly payments, or applications with a credit score below 620 are declined, whereas higher scores qualify for better interest rates. The following diagram illustrates the compliance agent workflow.
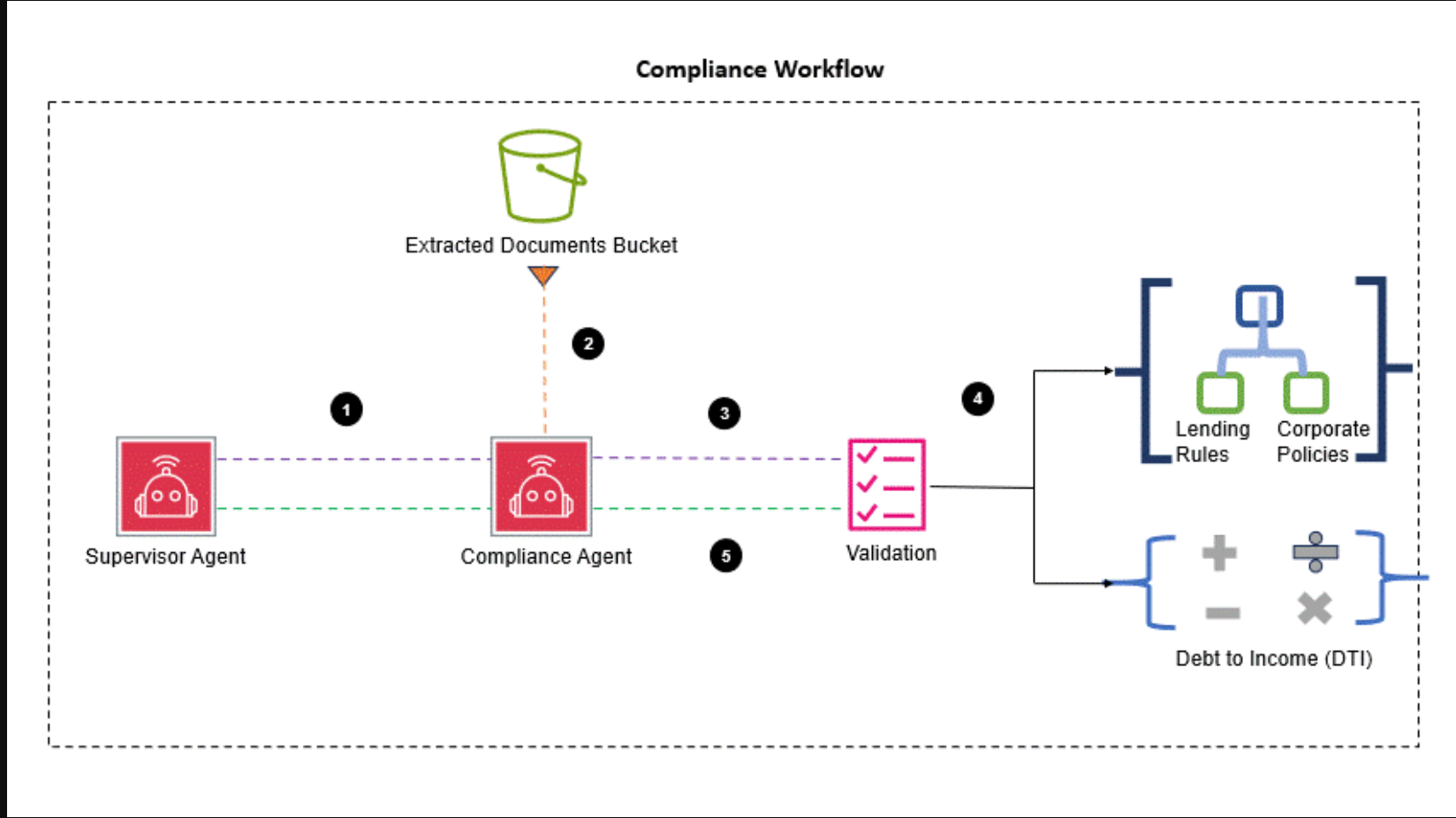
The workflow includes the following steps:
- The supervisor agent assigns the compliance validation task to the compliance agent.
- The compliance agent retrieves the applicant details stored in the extracted documents S3 bucket.
- The applicant details are validated against mortgage processing rules.
- The compliance agent calculates the applicant’s DTI ratio, applying corporate policy and lending rules to the application.
- The compliance agent uses the validated details to generate a status.
- The compliance agent sends the compliance status to the supervisor agent.
Underwriting agent
The underwriting agent generates an underwriting document for the underwriter to review. The underwriting agent workflow streamlines the process of reviewing and finalizing underwriting documents, as shown in the following diagram.
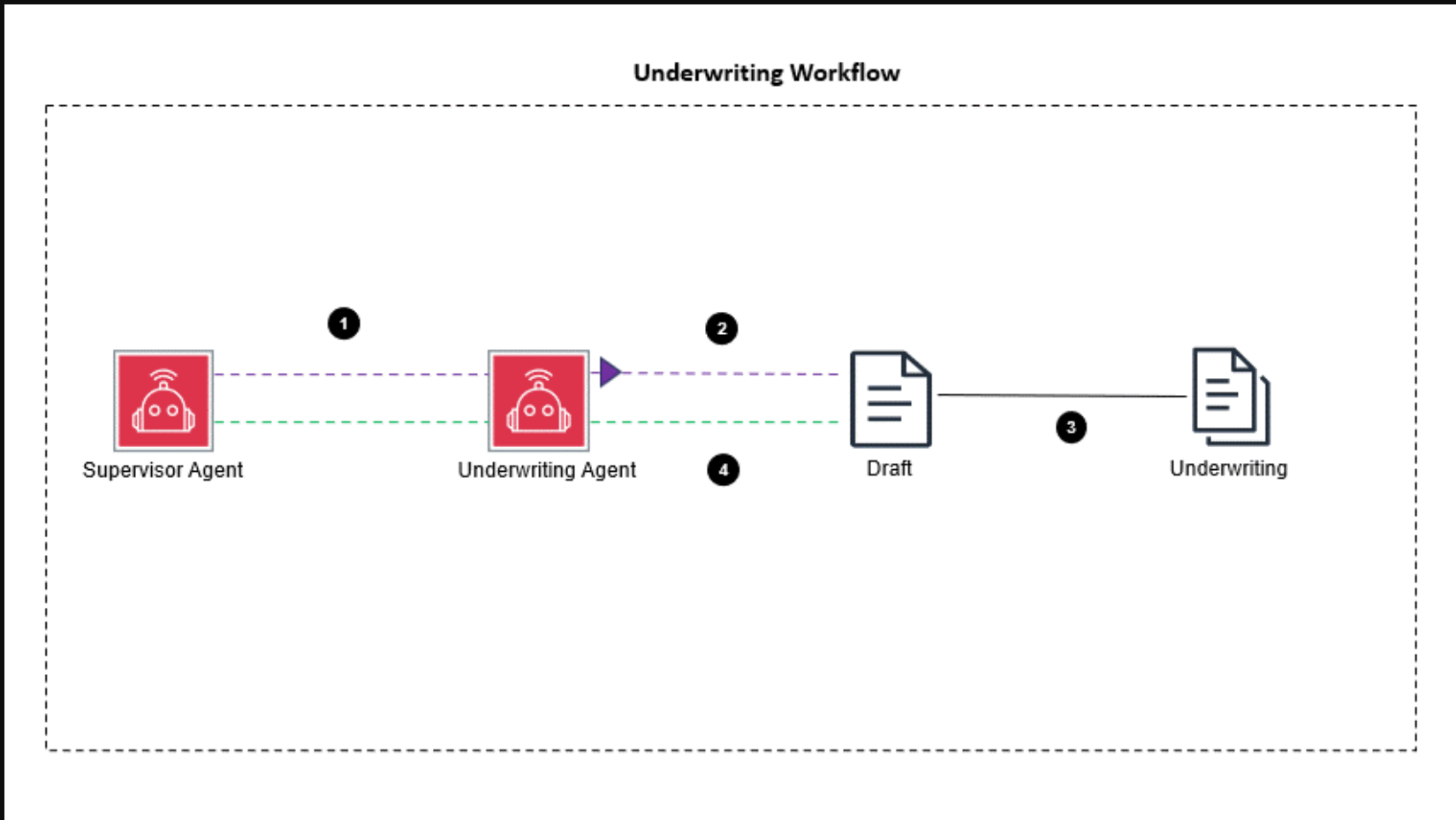
The workflow consists of the following steps:
- The supervisor agent assigns the underwriting task to the underwriting agent.
- The underwriting agent verifies the information and creates a draft of the underwriting document.
- The draft document is sent to an underwriter for review.
- Updates from the underwriter are sent back to the underwriting agent.
RACI matrix
The collaboration between intelligent agents and human professionals is key to efficiency and accountability. To illustrate this, we’ve crafted a RACI (Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, and Informed) matrix that maps out how responsibilities might be shared between AI-driven agents and human roles, such as compliance officers and the underwriting officer. This mapping serves as a conceptual guide, offering a glimpse into how agentic automation can enhance human expertise, optimize workflows, and provide clear accountability. Real-world implementations will differ based on an organization’s unique structure and operational needs.
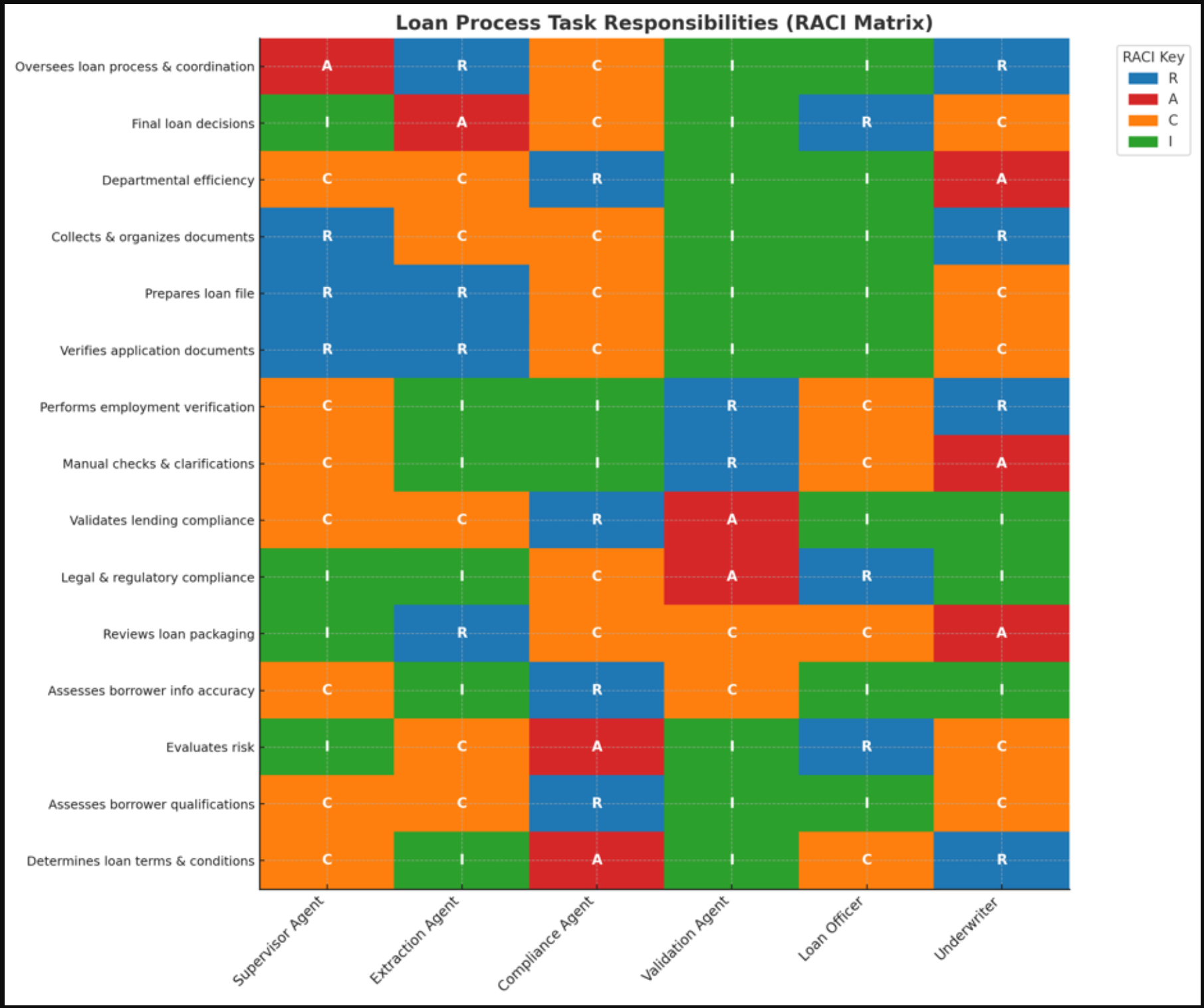
The matrix components are as follows:
- R: Responsible (executes the work)
- A: Accountable (owns approval authority and outcomes)
- C: Consulted (provides input)
- I: Informed (kept informed of progress/status)
End-to-end IDP automation architecture for mortgage processing
The following architecture diagram illustrates the AWS services powering the solution and outlines the end-to-end user journey, showcasing how each component interacts within the workflow.

In Steps 1 and 2, the process begins when a user accesses the web UI in their browser, with Amazon CloudFront maintaining low-latency content delivery worldwide. In Step 3, Amazon Cognito handles user authentication, and AWS WAF provides security against malicious threats. Steps 4 and 5 show authenticated users interacting with the web application to upload required documentation to Amazon S3. The uploaded documents in Amazon S3 trigger Amazon EventBridge, which initiates the Amazon Bedrock Data Automation workflow for document processing and information extraction.
In Step 6, AWS AppSync manages user interactions, enabling real-time communication with AWS Lambda and Amazon DynamoDB for data storage and retrieval. Steps 7, 8, and 9 demonstrate how the Amazon Bedrock multi-agent collaboration framework comes into play, where the supervisor agent orchestrates the workflow between specialized AI agents. The verification agent verifies uploaded documents, manages data collection, and uses action groups to compute DTI ratios and generate an application summary, which is stored in Amazon S3.
Step 10 shows how the validation agent (broker assistant) evaluates the application based on predefined business criteria and automatically generates a pre-approval letter, streamlining loan processing with minimal human intervention. Throughout the workflow in Step 11, Amazon CloudWatch provides comprehensive monitoring, logging, and real-time visibility into all system components, maintaining operational reliability and performance tracking.
This fully agentic and automated architecture enhances mortgage processing by improving efficiency, reducing errors, and accelerating approvals, ultimately delivering a faster, smarter, and more scalable lending experience.
Prerequisites
You need to have an AWS account and an AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) role and user with permissions to create and manage the necessary resources and components for this solution. If you don’t have an AWS account, see How do I create and activate a new Amazon Web Services account?
Deploy the solution
To get started, clone the GitHub repository and follow the instructions in the README to deploy the solution using AWS CloudFormation. The deployment steps offer clear guidance on how to build and deploy the solution. After the solution is deployed, you can proceed with the following instructions:
- After you provision all the stacks, navigate to the stack
AutoLoanAPPwebsitewafstackXXXXXon the AWS CloudFormation console. - On the Outputs tab, locate the CloudFront endpoint for the application UI.

You can also get the endpoint using the AWS Command Line Interface (AWS CLI) and the following command:
- Open the (
https://<domain_name>.cloudfront.net) in a new browser.

You should see the application login page.
- Create an Amazon Cognito user in the user pool to access the application.
- Sign in using your Amazon Cognito email and password credentials to access the application.

Monitoring and troubleshooting
Consider the following best practices:
- Monitor stack creation and update status using the AWS CloudFormation console or AWS CLI
- Monitor Amazon Bedrock model invocation metrics using CloudWatch:
InvokeModelrequests and latency- Throttling exceptions
- 4xx and 5xx errors
- Check Amazon CloudTrail for API invocations and errors
- Check CloudWatch for solution-specific errors and logs:
aws cloudformation describe-stacks —stack-name <stack-name>
Clean up
To avoid incurring additional costs after testing this solution, complete the following steps:
- Delete the relevant stacks from the AWS CloudFormation console.
- Verify the S3 buckets are empty before deleting them.
结论
示例自动贷款申请示例解决方案演示了如何使用Amazon Bedrock Agents和Amazon Bedrock Data Automation来转换抵押贷款处理工作流程。除了抵押贷款处理之外,您还可以调整此解决方案以简化索赔处理或解决其他复杂的文档处理场景。通过使用智能自动化,该解决方案大大减少了人工劳动,缩短了处理时间,并加快了决策过程。自动化这些复杂的工作流程有助于组织实现更高的运营效率,保持对不断发展的法规的一致遵守,并提供卓越的客户体验。
示例解决方案以开源形式提供——将其用作您自己解决方案的起点,并通过使用GitHub pull请求提供回修和功能来帮助我们使其更好。浏览GitHub存储库以浏览代码,单击watch以获取新版本的通知,并查看README以获取最新的文档更新。
作为下一步,我们建议评估您当前的文档处理工作流程,以确定适合使用Amazon Bedrock Agents和亚马逊Bedrock Data automation进行自动化的领域。
如需专家帮助,AWS专业服务和其他AWS合作伙伴将提供帮助。
我们很乐意收到你的来信。请在评论区告诉我们您的想法,或使用存储库中的问题论坛。
- 登录 发表评论
- 6 次浏览
最新内容
- 1 month 2 weeks ago
- 1 month 2 weeks ago
- 1 month 2 weeks ago
- 1 month 2 weeks ago
- 1 month 2 weeks ago
- 1 month 2 weeks ago
- 1 month 2 weeks ago
- 1 month 2 weeks ago
- 1 month 2 weeks ago
- 1 month 2 weeks ago